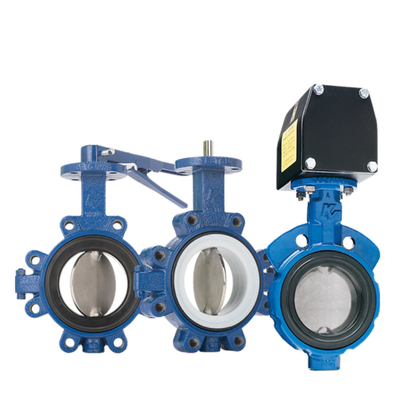
Valve Positioner vs Position Transmitter: Key Differences Explained
In industrial automation, engineers often confuse valve positioners and position transmitters, leading to suboptimal setups in control loops. While both relate to valve stem position, their roles differ fundamentally—one acts, the other observes. Drawing from 20 years of field troubleshooting in petrochemical plants, I'll break down the difference between valve positioner and position transmitter, covering working principles, core distinctions, applications, and common pitfalls. This guide aims to clarify why mixing them up can spike energy costs or trigger false alarms, using real-world examples and diagrams.
The Essence: What They Are and How They Work
A valve positioner is an active controller that receives a control signal (e.g., 4-20 mA) and adjusts the actuator's air pressure to precisely position the valve stem, compensating for hysteresis, friction, or pressure drops. Its valve positioner working principle revolves around a closed-loop system: feedback from the stem (via linkage or sensor) is compared to the setpoint, and the positioner modulates output until they match. For instance, in pneumatic types, a flapper-nozzle creates backpressure to shift a relay, delivering air to the diaphragm. Digital versions like Fisher DVC6200 add PID algorithms for faster response (<0.3 sec) and diagnostics.
In contrast, a position transmitter is a passive sensor that measures stem position and converts it to an output signal (e.g., 4-20 mA or digital) for monitoring or feedback to a PLC/DCS. The position transmitter principle is straightforward: a potentiometer, LVDT, or Hall effect sensor detects linear/rotary movement, scaling it to the signal range. No adjustment occurs—it's purely indicative, like a speedometer showing velocity without controlling the engine.
From my refinery projects, positioners solve dynamic issues (e.g., actuator stick-slip), while transmitters provide data for trend analysis.
Core Differences: A Head-to-Head Comparison
Here's where many specs get crossed. Positioners are "doers," transmitters "reporters." Key contrasts:
| Aspect |
Valve Positioner |
Position Transmitter |
| Function |
Controls actuator to achieve desired position |
Measures and transmits current position |
| Loop Role |
Closed-loop feedback controller |
Open-loop sensor for monitoring |
| Input/Output |
Input: Control signal; Output: Actuator pressure |
Input: Stem movement; Output: Signal (4-20 mA) |
| Principle |
Force/motion balance with adjustment |
Linear conversion (e.g., resistance to current) |
| Accuracy |
±0.1-0.5% with tuning |
±0.25-1% depending on sensor |
| Power Requirement |
Loop-powered or external (pneumatic/electric) |
Typically loop-powered |
| Common Types |
Pneumatic, electro-pneumatic, digital |
Analog (potentiometer), digital (Hall) |
Positioners tackle nonlinearities like deadband (up to 5% reduction), while transmitters shine in diagnostics without control intervention. In a gas compressor setup I handled, swapping a transmitter for a positioner fixed overshoot issues.
Application Scenarios: When to Use Each
- Valve Positioner: Essential in active control loops where precision matters. Use in throttling applications like flow regulation in chemical reactors or pressure control in oil pipelines. Ideal for large actuators or high-friction valves, reducing energy waste by 10-20% through tight positioning.
- Position Transmitter: Best for monitoring and verification. Deploy in safety systems to confirm valve status (e.g., open/closed in ESD loops) or integrate with SCADA for remote oversight in water treatment plants. Not for direct control—it's like a dashboard gauge, not the steering wheel.
In power generation, positioners handle boiler feedwater modulation; transmitters monitor isolation valve states for compliance audits.
Why put a 4-20mA position transmitter on a Control Valve
Common Customer Misconceptions and How to Avoid Them
Misconception 1: "They're interchangeable." Reality: Installing a transmitter instead of a positioner leads to poor regulation—e.g., a client in pharma saw 15% process variance until we retrofitted a positioner.
Misconception 2: "Transmitters provide control." No—they only report. In high-ΔP scenarios, without a positioner's adjustment, actuators drift, causing leaks or inefficiency.
Misconception 3: "Digital versions are always better." While smart positioners add diagnostics, basic transmitters suffice for simple monitoring, saving costs.
Tip: Always check loop requirements—control needs positioners; pure feedback favors transmitters. From my audits, 30% of issues stem from this mix-up.
Xiangjing: Your Go-To Supplier for Valve Positioners and Transmitters
As one of China's largest valve positioner suppliers, Xiangjing offers a rich selection of brands and models with ample inventory for fast delivery. We provide competitive pricing, reliable lead times, and expert technical support to resolve your control challenges. Visit our official website at www.shgongboshi.com for quotes on valve positioners and transmitters.
Keywords: valve positioner vs position transmitter, difference between valve positioner and position transmitter, valve positioner working principle, position transmitter principle, valve positioner applications, position transmitter uses, pneumatic valve positioner vs transmitter, digital valve positioner differences.

 ข้อความของคุณจะต้องอยู่ระหว่าง 20-3,000 ตัวอักษร!
ข้อความของคุณจะต้องอยู่ระหว่าง 20-3,000 ตัวอักษร! กรุณาตรวจสอบอีเมลของคุณ!
กรุณาตรวจสอบอีเมลของคุณ!  ข้อความของคุณจะต้องอยู่ระหว่าง 20-3,000 ตัวอักษร!
ข้อความของคุณจะต้องอยู่ระหว่าง 20-3,000 ตัวอักษร! กรุณาตรวจสอบอีเมลของคุณ!
กรุณาตรวจสอบอีเมลของคุณ! 







